How Immutable Backups Protect Against Ransomware Attacks
Data is the lifeblood of businesses, governments, and our virtual lives, which makes its security crucial. With 1,815 undisclosed ransomware attacks reported in the first six months of 2023, the need for robust data protection strategies is more critical than ever.
Immutable backups have emerged as a central strategy in safeguarding credentials against malicious attacks, ensuring that organizations have a secure and unalterable copy of their data to fall back on if, or rather when, the disaster strikes.
Let’s dive into the article to learn more about how it protects important information!
Understanding Immutable Backups
Immutable backup refers to a data storage state that is fixed, unchangeable, and undeletable once stored. Historically, the concept existed even during the days of tape cache, where tapes were physically set to write once and read many (WORM), thereby making them rigid.
Once an organization stores a backup, it remains unaltered, providing a vital layer of protection from malware.
An unchangeable repository ensures that info is impervious to virus infections, and by maintaining archives of immutable backups, organizations can guarantee recovery from malware strikes by reverting to a clean, secure support
The concept of backups is particularly pivotal in sectors where info integrity is paramount, such as healthcare, finance, and government operations. Organizations can confidently validate the authenticity and reliability of the data during recovery, which maintains regulatory compliance and trust.
This structured approach not only facilitates easier recovery but also ensures that organizations are better positioned to manage their lifecycle effectively.
The Significance of Immutable Backups in Ransomware Defense
Ransomware attacks are notorious for encrypting or locking access to an organization’s data, demanding a ransom for its release. In recent years, these assaults have evolved to infiltrate backups, rendering traditional strategies ineffective.
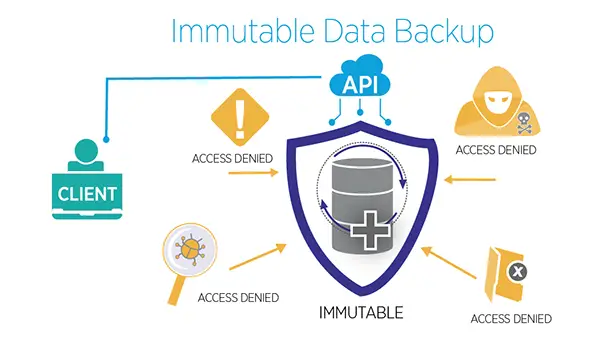
The backups, with their inherent characteristic of being unalterable, provide a reliable defense mechanism against such strikes. Even if a cyberattack manages to compromise the live info, it remains untouched, providing a secure point to which the system can be restored.
With malware attacks surging by over 37% in 2023 and the average enterprise ransom payment soaring above $100,000, the financial implications of these are substantial, making the role of backups in ransomware defense all the more crucial.
In this scenario, you could imagine immutable backups as a time capsule, which, upon its burial, remains unchanged and untouched until its point of retrieval.
Implementing an Immutable Backup Strategy
Implementing an immutable backup strategy involves several key considerations:
Data Integrity
Data integrity in the backup master plan is pivotal. This involves making certain that the platform used for storing information is secure and resilient to various forms of cyberattacks, especially malware.
The essence of maintaining data integrity lies in the assurance that it retains its original form and details.
This means that even in the face of a cyberattack, the stored info remains reliable and true to its original state, free from unauthorized modifications or deletions, thereby providing a reliable restore point in the event of data loss or corruption.
Zero Trust Model
The Zero Trust Model revolves around strict user authentication and verification processes when trying to access data backups.
This model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify”. This means that trust is never assumed and verification is mandatory for every access attempt, regardless of where the request originates from.
Even within private networks, every user trying to access the backup must undergo strict identity verification processes.
This often involves employing multifactor authentication and other advanced security protocols to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the info, thereby safeguarding the data from internal and external threats.
Multi-Level Resiliency
Multi-level resiliency is about establishing a comprehensive defense plan that intertwines the robustness of backups with advanced cybersecurity technologies and continuous employee training.
Advanced cybersecurity technologies provide additional layers of defense to combat potential threats.
Incorporating cybersecurity technologies like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) can significantly bolster multi-level resiliency by providing real-time monitoring and response to potential threats across all network endpoints and traffic.
On top of that, regular employee training ensures that the human element, often considered the weakest link in cybersecurity, is fortified, thereby enhancing the overall resiliency of the protection strategy.
Automated Response
An automated response system is crucial in providing an immediate reaction to threats, especially during off-hours when immediate human intervention may not be possible.
Developing systems that can autonomously respond to threats, such as identifying and quarantining infected systems, ensures that the spread of ransomware or other malware is halted as soon as it is detected.
An automated response system can also initiate predefined recovery processes, thereby reducing downtime and mitigating the impact of the attack.
Clean Restore Point
A clean restore point involves guaranteeing that the backups are free from malware before storage and safeguarded from encryption to ensure clean recovery.
This means that before data is backed up, it is thoroughly scanned and verified to be free from any form of malware or inconsistencies. Organizations can be assured that in the event of a virus attack, they have a secure and clean version of their information to revert to.
This ensures that the recovery process is smooth and that the restored data is reliable and free from threats, thereby safeguarding the continuity of business operations.
Additionally, utilizing encryption technologies ensures that even if the info is intercepted or accessed unauthorized, it remains unintelligible and useless to the attackers.
Immutable Backup in Cloud Storage
Cloud storage has become a popular medium in modern backup architectures. The cloud provides scalability, durability, and resilience, offering substantial bandwidth between compute nodes.
However, it’s imperative to ensure that it adheres to the principles of immutability, preventing unauthorized deletion or modification of the data, even by administrators.
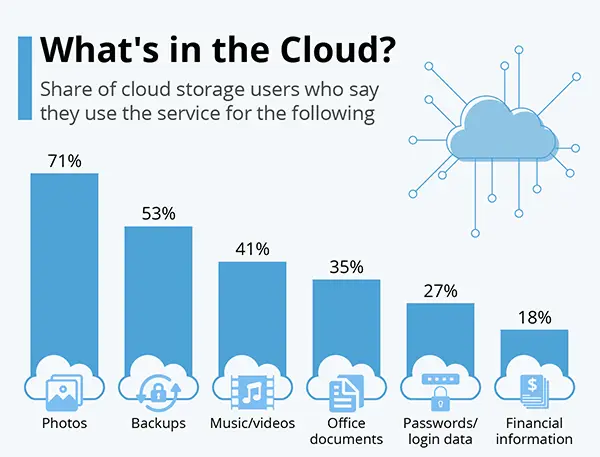
The above statistics show the features of cloud storage.
Incorporating it into the reinforcement strategy also brings forth the advantage of geographical redundancy, wherein data is stored in multiple locations, safeguarding from regional outages or disasters.
The providers often have strict security protocols and regular audits to shield the data with the latest security mechanisms. It also allows organizations to enjoy cost-effectiveness.
Moreover, it facilitates easier management and monitoring of backups, providing a streamlined approach to info management and recovery.
Immutable Backups: A Foundation, Not a Cure-All
While these are a cornerstone in a robust cybersecurity strategy, they should be part of a multi-faceted approach to data protection, especially for dynamic sectors like e-commerce, where it is a valuable asset.
To know more about developing secure e-commerce platforms that can integrate such cybersecurity strategies, visit our detailed guide.
This comprehensive approach includes adhering to the 3-2-1 backup rule, data integrity, employing a zero-trust model, and multi-level resiliency by combining technology with employee training.
Moreover, organizations must be cognizant of the potential drawbacks of this help, such as susceptibility to physical damage if stored on-premises, potential redirection of backups during a live mount, and the costs associated with cloud storage hosting over time.
Wrapping Up
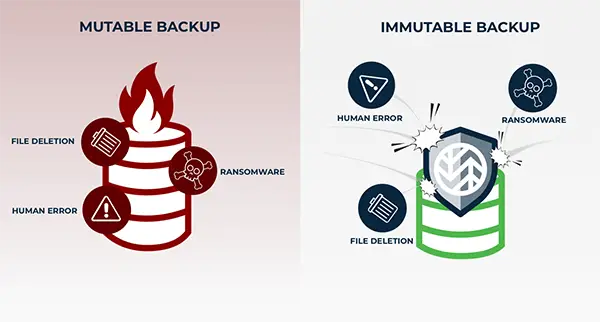
Immutable backups emerge as a robust shield in the digital realm, protecting from the menacing claws of malware strikes. Their unalterable nature ensures that organizations always possess a pure, untainted sanctuary for their info, even amidst the chaos of cyber threats.
While they stand firm, providing a reliable fallback in crises, their true potency is unleashed when integrated into a comprehensive, multi-layered cybersecurity strategy.
Thus, immutable backups serve as a secure data haven and symbolize the resilience and strategic foresight required in our interconnected digital age.
Share